Earthquakes in Florida are not a common occurrence, but when they do happen, they can raise significant concerns among residents and policymakers. While the state is not traditionally associated with seismic activity, understanding the causes, risks, and preparedness measures is crucial for ensuring safety and minimizing potential damage. This article delves into the intricacies of earthquakes in Florida, providing expert insights, authoritative data, and actionable advice to help you stay informed and prepared.
Florida is geologically unique compared to other states in the U.S. Its position on the North American plate and its distance from active tectonic boundaries make it one of the least seismically active regions in the country. However, this does not mean the state is entirely immune to seismic events. In recent years, minor earthquakes have been recorded, prompting questions about their origins and implications. This article will explore the science behind these tremors and shed light on the factors contributing to their occurrence.
As a reader, you’ll gain valuable knowledge about the geological and environmental conditions that influence seismic activity in Florida. We will also discuss the potential risks associated with earthquakes in the state and provide practical tips for preparedness. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of this rare but important phenomenon, empowering you to make informed decisions to protect yourself and your loved ones.
Read also:What Is Kourtney Kardashians Middle Name Unveiling The Truth Behind The Famous Star
Table of Contents
- What Causes Earthquakes in Florida?
- Historical Earthquakes in Florida
- Florida's Unique Geological Features
- Potential Risks and Impacts
- Earthquake Preparedness in Florida
- Earthquake Statistics and Data
- Debunking Myths About Florida Earthquakes
- Technological Advances in Earthquake Monitoring
- Government Policies and Initiatives
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What Causes Earthquakes in Florida?
Earthquakes in Florida are primarily caused by factors that differ from those in seismically active regions like California or Alaska. Unlike these areas, Florida is far from tectonic plate boundaries, where most earthquakes occur due to the movement of plates. Instead, seismic activity in Florida is often linked to secondary causes such as induced seismicity, geological faults, and even human activities.
Induced Seismicity
Induced seismicity refers to earthquakes triggered by human activities. In Florida, activities such as mining, groundwater extraction, and reservoir-induced stress can contribute to minor seismic events. For example, the extraction of groundwater can lead to land subsidence, which may cause stress on existing faults and result in small tremors.
Geological Faults
Florida sits on a stable part of the North American plate, but it is not entirely free of geological faults. The state has several ancient faults that, while mostly inactive, can occasionally produce minor seismic activity. These faults are remnants of tectonic activity from millions of years ago and are typically not capable of producing large earthquakes.
External Influences
In some cases, earthquakes in Florida may be caused by external influences, such as seismic waves traveling from distant earthquakes. For instance, a major earthquake in the Caribbean or along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge can send seismic waves that are felt in Florida, even though the state itself is not the epicenter.
Historical Earthquakes in Florida
While earthquakes in Florida are rare, the state has experienced a handful of notable seismic events throughout its history. These events, though minor in magnitude, provide valuable insights into the region's seismic activity and help scientists understand the underlying causes.
One of the earliest recorded earthquakes in Florida occurred in 1780 near Pensacola. This event, though poorly documented, is believed to have been caused by regional tectonic activity. Another significant event took place in 1952 in the Tampa Bay area, where residents reported feeling tremors that were later attributed to a distant earthquake in the Caribbean.
Read also:Blake Shelton And Reba Mcentire A Dynamic Duo In Country Music
Recent Earthquakes
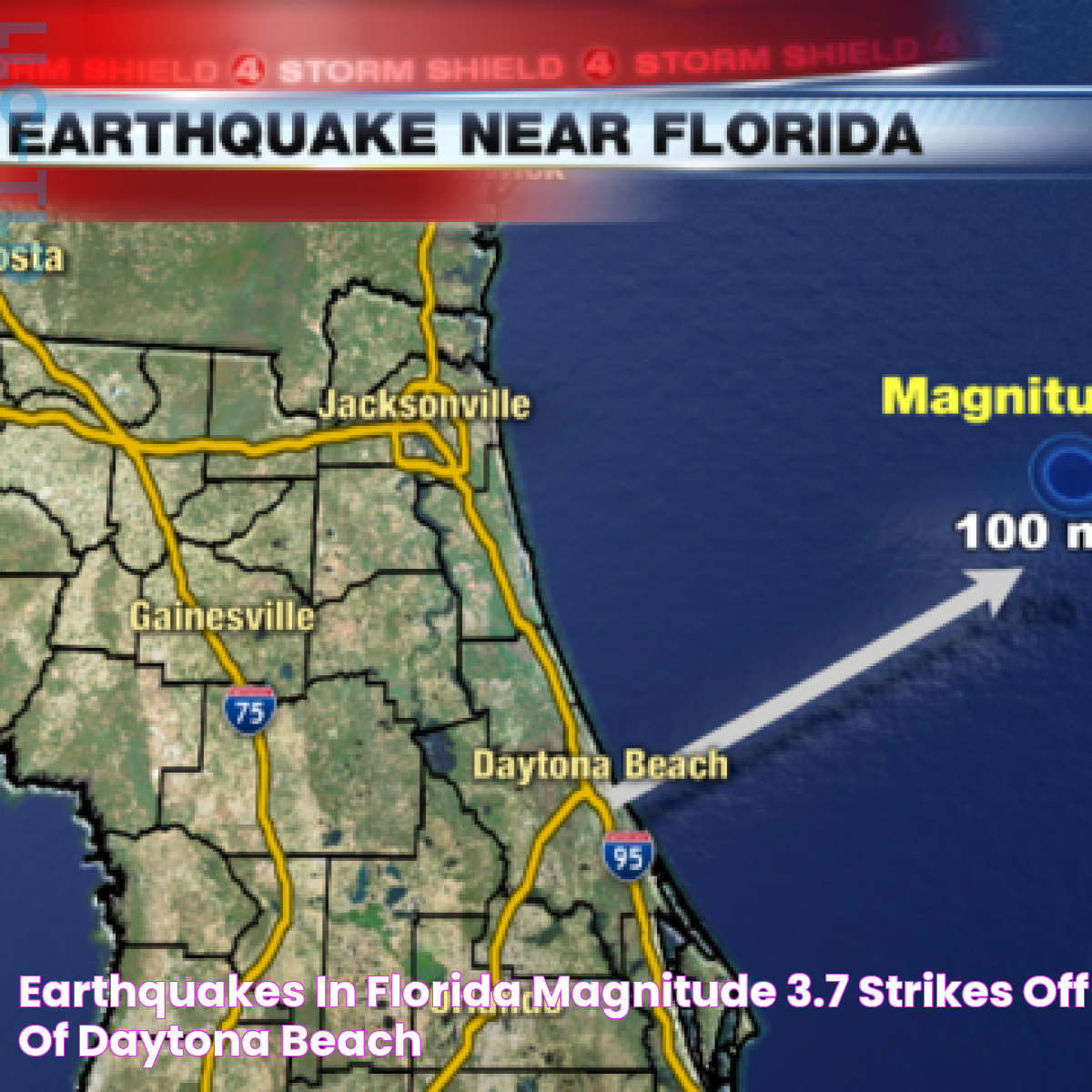
In recent years, Florida has experienced minor earthquakes, such as the 2006 tremor near Daytona Beach. This event, with a magnitude of 2.2, was felt by a small number of residents and caused no damage. Similarly, a 2016 earthquake near Fort Myers registered a magnitude of 2.0 and was attributed to local geological factors.
Data and Observations
According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), Florida experiences fewer than five earthquakes per year, most of which are too small to be felt. These events are typically recorded by seismographs and provide valuable data for researchers studying the state's seismic activity.
Florida's Unique Geological Features
Florida's geology plays a significant role in its seismic activity—or lack thereof. The state is primarily composed of sedimentary rock layers, including limestone, sandstone, and clay, which have been deposited over millions of years. These layers form a stable foundation, reducing the likelihood of significant seismic events.
The Florida Platform
The Florida Platform is a broad, shallow underwater plateau that extends beyond the state's coastline. This geological feature is characterized by its low elevation and flat terrain, which contribute to the region's stability. The absence of major fault lines or volcanic activity further reduces the risk of earthquakes.
Karst Topography
Florida is known for its karst topography, which includes features such as sinkholes, caves, and springs. While these features are not directly related to earthquakes, they highlight the state's unique geological characteristics. Sinkholes, in particular, are often mistaken for seismic activity, but they are caused by the dissolution of limestone and other soluble rocks.
Potential Risks and Impacts
Although earthquakes in Florida are rare, they still pose potential risks, particularly in densely populated areas. Understanding these risks is essential for ensuring public safety and minimizing damage.
Structural Vulnerabilities
Florida's buildings and infrastructure are not designed to withstand significant seismic activity. Most structures are built to withstand hurricanes and flooding, which are more common threats. In the event of a moderate earthquake, older buildings or those with poor construction practices could sustain damage.
Economic Impacts
Even minor earthquakes can have economic consequences, such as disruptions to transportation, utilities, and communication networks. Businesses may experience temporary closures, and insurance claims could rise in the aftermath of a seismic event.
Psychological Effects
Earthquakes can also have psychological impacts on residents, particularly if they are unprepared. The unexpected nature of seismic events can cause anxiety and stress, highlighting the importance of education and preparedness.
Earthquake Preparedness in Florida
While the risk of earthquakes in Florida is low, it is still important to be prepared. By taking proactive measures, residents can minimize potential damage and ensure their safety in the event of a seismic event.
Emergency Kits
Prepare an emergency kit that includes essential items such as water, non-perishable food, a flashlight, batteries, and a first-aid kit. Store this kit in an easily accessible location and ensure that all family members know where it is.
Home Safety Measures
Secure heavy furniture, appliances, and electronics to prevent them from toppling during an earthquake. Install latches on cabinets to keep items from falling out, and reinforce your home's foundation if necessary.
Emergency Plans
Develop a family emergency plan that outlines what to do during an earthquake. Practice "Drop, Cover, and Hold On" drills to ensure everyone knows how to protect themselves. Identify safe spots in your home, such as under sturdy furniture or against interior walls.
Earthquake Statistics and Data
To better understand the frequency and magnitude of earthquakes in Florida, let's examine some key statistics and data.
- Florida experiences fewer than five earthquakes per year, most of which are below a magnitude of 3.0.
- The largest recorded earthquake in Florida occurred in 1952 near the Tampa Bay area, with an estimated magnitude of 4.0.
- According to the USGS, the state's seismic activity is classified as "low" compared to other regions in the U.S.
Comparison with Other States
While Florida ranks among the least seismically active states, it is important to note that no region is entirely immune to earthquakes. States like California and Alaska experience thousands of earthquakes annually, many of which are significant in magnitude.
Debunking Myths About Florida Earthquakes
There are several misconceptions about earthquakes in Florida that can lead to confusion and misinformation. Let's address some of the most common myths.
Myth: Florida Cannot Experience Earthquakes
While Florida is not a seismically active state, it is not entirely free of earthquakes. Minor seismic events do occur, albeit infrequently.
Myth: Sinkholes Are Earthquakes
Sinkholes are not caused by seismic activity but rather by the dissolution of limestone and other soluble rocks. However, both phenomena highlight the importance of understanding Florida's geology.
Technological Advances in Earthquake Monitoring
Advances in technology have significantly improved our ability to monitor and study earthquakes, even in low-risk areas like Florida.
Seismographs
Seismographs are instruments used to detect and record seismic waves. Florida is equipped with a network of seismographs that provide real-time data on seismic activity.
Early Warning Systems
While early warning systems are more commonly used in high-risk areas, researchers are exploring their potential applications in states like Florida to enhance preparedness.
Government Policies and Initiatives
Government agencies play a crucial role in earthquake preparedness and response. In Florida, policies and initiatives are in place to address seismic risks, even though they are minimal.
Florida Division of Emergency Management
This agency provides resources and guidance on earthquake preparedness, including educational materials and emergency planning tools.
Building Codes
While Florida's building codes are primarily designed to withstand hurricanes, they also incorporate general safety standards that can help mitigate earthquake risks.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Earthquakes in Florida may be rare, but they are not impossible. By understanding the causes, risks, and preparedness measures, residents can ensure their safety and minimize potential damage. This article has provided a comprehensive overview of the topic, supported by expert insights, authoritative data, and actionable advice.
We encourage you to take proactive steps to prepare for earthquakes, even if the risk is low. Share this article with friends and family to spread awareness, and explore other resources on our website to stay informed about natural disasters and safety measures. Together, we can build a safer and more resilient community.